Electrical Energy Waste at Home: Causes, Costs and Prevention Tips
Top 5 Causes Of Electricity Wastage
- HVAC Air Conditioning
- Water Heating
- Appliances
- Lighting
- Electronics
Defining Electrical Energy Waste
Electrical energy waste refers to the excessive and inefficient use of electricity in homes. It happens whenever we use more energy than necessary to perform tasks or power appliances and electronics. Some common scenarios include:
- Leaving lights, appliances, or devices turned on when not in use
- Using inefficient incandescent light bulbs instead of LEDs
- Having an improperly sized heating/cooling system that consumes more energy to maintain temperature
- Allowing appliances and electronics to run in standby mode
- Using older, inefficient models of refrigerators, washing machines, and other major appliances
These habitual behaviors and outdated technologies lead to substantial energy waste daily, accumulating over weeks, months, and years. With conscious effort and minor lifestyle changes, households can significantly reduce misused energy.
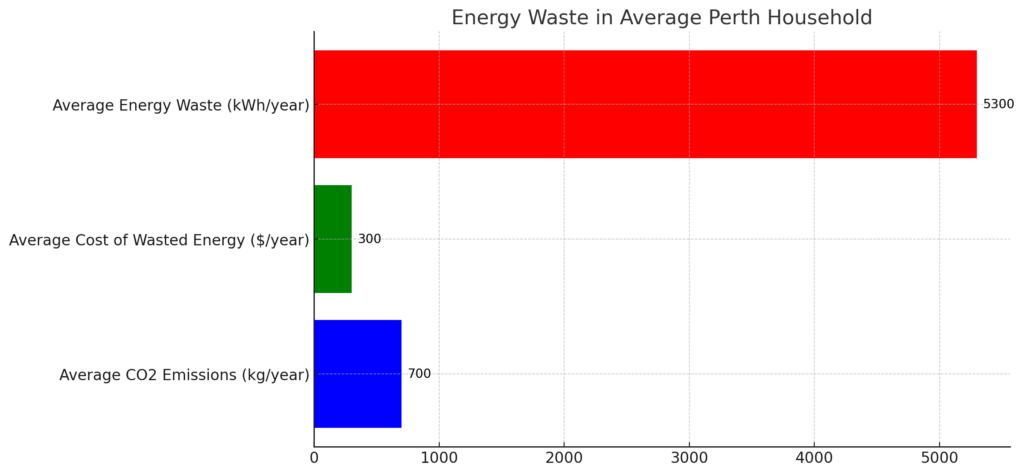
The High Cost of Wasted Energy
Electrical energy waste costs homeowners money. The average Perth household spends over $2,000 annually on electricity bills. However, studies show that 20% or more of this energy usage is wasted. For a household with a $100 monthly electricity bill, that’s $240 wasted per year.
Standby power or “phantom” draw also contributes to energy waste. Appliances like televisions, gaming consoles, and cable boxes use power even when switched off. This can add up to 10% of electricity costs, around $25 per month or $300 annually for average homes. The cumulative cost of wasted energy is enough to purchase new energy-efficient appliances over time.
Energy Savings Estimator
Results:
Monthly Savings: $
Annual Savings: $
Need A Electrician In Perth?
BOOK ONLINE TODAY
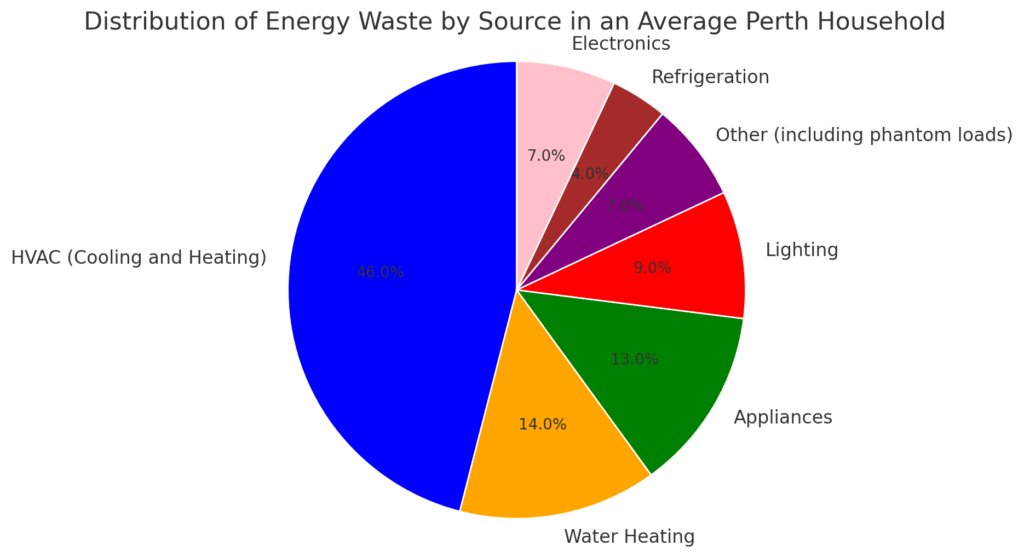
Common Causes of Energy Waste at Home
Electrical energy waste costs homeowners money. The average US household spends over $2,000 annually on electricity bills. However, studies show that 20% or more of this energy usage is wasted. For a household with a $100 monthly electricity bill, that’s $240 wasted per year.
Standby power or “phantom” draw also contributes to energy waste. Appliances like televisions, gaming consoles, and cable boxes use power even when switched off. This can add up to 10% of electricity costs, around $25 per month or $300 annually for average homes. The cumulative cost of wasted energy is enough to purchase new energy-efficient appliances over time.
Section 3: Common Causes of Energy Waste at Home
There are several habitual behaviors and outdated technologies that lead to excessive electrical energy use in homes:
Lighting – Forgoing to turn off lights when leaving a room, using inefficient bulbs like incandescents and halogens instead of LEDs, and having too many lights turned on at once all contribute to waste.
Appliances – Leaving appliances like televisions, stoves, and irons plugged in when not in use leads to standby energy drain. Using old, inefficient appliances instead of Energy Star-rated models uses more electricity.
Electronics – Game consoles, laptops, phone chargers and other electronics that are left plugged in or on standby mode use phantom power.
HVAC Systems – Improperly sized heating/cooling systems that frequently cycle on and off use more energy. Old units with low SEER ratings are inefficient.
Laundry – Washing smaller loads, using hot water cycles excessively, and drying without fully loading machines wastes energy.
Refrigeration – Old refrigerators and freezers with poor insulation and seals use 15% or more power. Units located near heat sources run longer.
Water Heating – Faucet leaks and dripping hot water taps waste heated water and electricity. Poorly insulated tanks and pipes lose heat.
Cooking – Using large appliances like ovens and ranges for small meals, not turning items off immediately after cooking, and not using lids causes waste.
Phantom Loads – Devices plugged into outlets use energy even when switched off. These phantom loads account for 5-10% of electricity use.
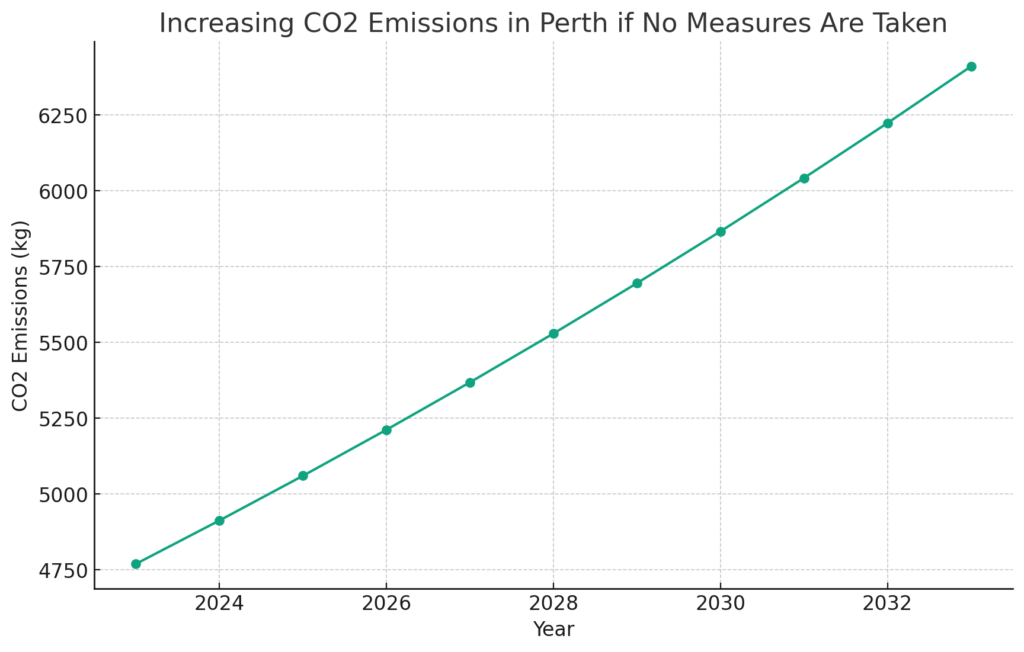
Local Environmental Impact in Perth
Wasting electricity has major negative environmental impacts, including here in Perth. According to Western Australia’s largest electricity provider Synergy, the average Perth household uses around 5,300 kWh of electricity per year. A significant portion of this is wasted through inefficient use.
Most of Perth’s electricity is generated by burning coal and natural gas, which releases greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Synergy estimates that every 1 kWh of electricity used in Perth homes produces around 0.9 kg of CO2 emissions. This means if the average household cuts their electrical waste by 15% or 800 kWh per year, they could reduce their annual CO2 emissions by over 700 kg.
Across all of Perth’s 500,000 households, a 15% reduction in energy waste would save over 400 million kWh of electricity use annually. This equates to cutting local CO2 emissions by more than 350 million kg per year, equal to taking over 70,000 cars off the road. Simple behavioral changes can result in significant benefits in reducing Perth’s carbon footprint. Conserving electricity helps combat climate change and preserves local resources.
Strategies to Reduce Energy Waste
Many energy waste issues can be corrected through minor lifestyle and behavioral adjustments:
Replace all light bulbs with efficient LEDs and turn off lights when leaving rooms to cut lighting waste by over 75%. Use natural light and task lighting.
Unplug devices like TVs, laptops, and phone chargers when not in use or use smart power strips to cut phantom loads.
Replace old appliances and HVAC systems with Energy Star-rated models to maximize efficiency. Properly size HVAC units.
Run full loads in washers, dryers, and dishwashers and use energy-saver settings to cut usage 25%. Hang-dry clothing to avoid dryer use.
Set refrigerators at 37°F and freezers at 0°F. Regularly defrost and clean coils. Replace old units.
Use lids on pots and pans when cooking and turn off appliances immediately after use. Use smaller appliances for small meals.
Install low-flow showerheads and faucet aerators. Fix leaks. Insulate hot water pipes and tanks. Lower water heater temperature.
Utilize advanced power strips, timers, motion sensors, and smart home technology to automatically reduce phantom and standby loads.
Need A Electrician In Perth?
BOOK ONLINE TODAY
Understanding Phantom Loads
Phantom load, also called standby power or vampire power draw, is electricity consumed by appliances and devices even when switched off or not actively being used. These loads occur because modern electronics use external low-voltage DC power adapters that continue drawing current when plugged into AC outlets.
Common sources of phantom loads include:
- Computers and monitors
- Modems and routers
- Printers and scanners
- Video game consoles
- Televisions and DVD players
- Cable and satellite boxes
- Cell phone chargers
- Digital clocks
- Coffee makers, microwaves and other appliances with clocks
A single device may only draw a few watts on standby. However, most homes have dozens of electronics plugged into outlets 24/7. This can lead to 100 to 300 watts of phantom loads continuously, adding nearly $100 per year in wasted electricity costs.
Conclusion
There are many simple and effective ways households can identify and reduce electrical energy waste on a daily basis. By replacing inefficient lighting and appliances, modifying behaviors, and being mindful of phantom loads, significant energy and cost savings can be achieved while also minimizing environmental impacts. With some effort, any home can utilize electricity in a smarter, more efficient manner for a more sustainable future.




